Fuel for Reactors of the Future
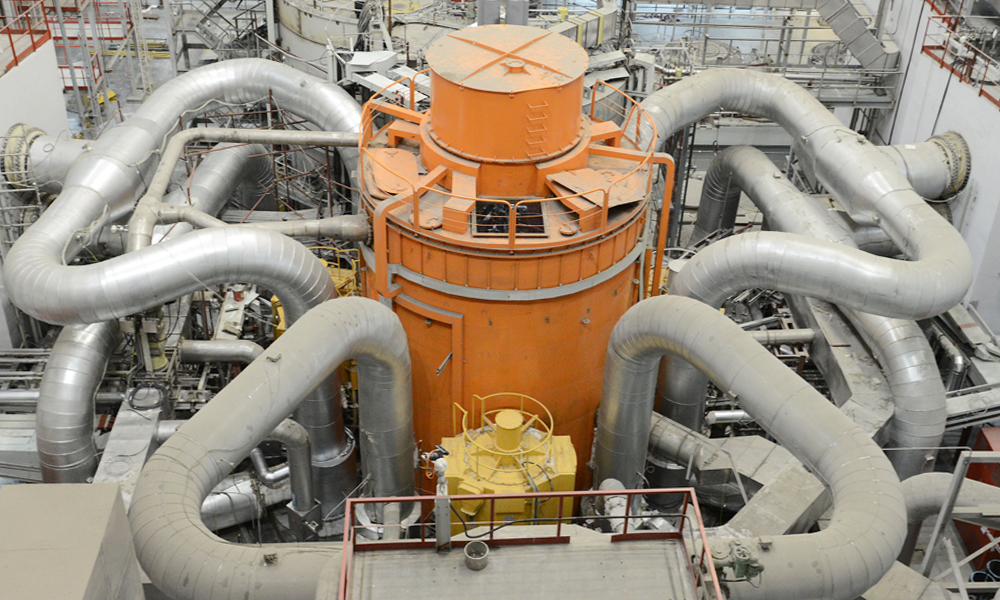
back to contentsBN-800 at Beloyarsk Unit 4 is designed to pilot test and fine tune nuclear technologies of the future. Having an installed capacity of 800 MW, Beloyarsk Unit 4 with the BN-800 fast breeder generated its first electricity in December 2015 and was brought online on 31 October 2016.
BN-800 will be used to pilot test the closed nuclear fuel cycle technology. In the closed nuclear cycle, fuel is reproduced, or bred, in fast reactors, thus increasing the fuel stock in the industry and minimizing radioactive waste by ‘burning up’ hazardous radionuclides.
According to experts, Russia is a global leader in fast breeder technologies. The BN-800 reactor unit is a prototype for more powerful commercial reactors labeled BN-1200. Any decision on the feasibility of their construction will depend on the experience gained from the operation of BN-800.
RIAR has fulfilled its annual production plan for 2016 in mid-November. “A sizable contribution to the fulfillment of our annual plan for 2016 was the production of fuel rods to be loaded into the BN-800 core. In 2016, we manufactured and shipped 38 fuel assemblies for a total of 619 million rubles,” RIAR’s report says. BN-800 is designed to run on the so-called mixed uranium plutonium oxide (MOX) fuel containing plutonium recovered from spent nuclear fuel of thermal reactors, which are now a backbone of the present-day nuclear power industry.
A MOX fuel production facility for BN-800 was officially opened in 2015 at Rosatom’s Mining and Chemical Plant in Zheleznogorsk (Krasnoyarsk Krai). Since the decision to establish a MOX fabrication facility was somewhat delayed as compared to the overall BN-800 planning process, the first fuel load contained conventional uranium oxides. At present, only a portion of fuel assemblies (about one sixth) contains MOX fuel produced by RIAR and Rosatom’s another subsidiary, Mayak (Ozersk, Chelyabinsk Region). Mayak manufactured fuel rods with pelletized MOX fuel, while RIAR fabricates the so-called vibro-packed MOX fuel rods. The both types of fuel rods were assembled at RIAR. A switchover to MOX fuel is planned to be completed by 2019. The Research Institute of Atomic Reactors (a part of Rosatom’s research division) is Russia’s largest nuclear research center. RIAR operates a number of research reactors.