Reactors for Medicine
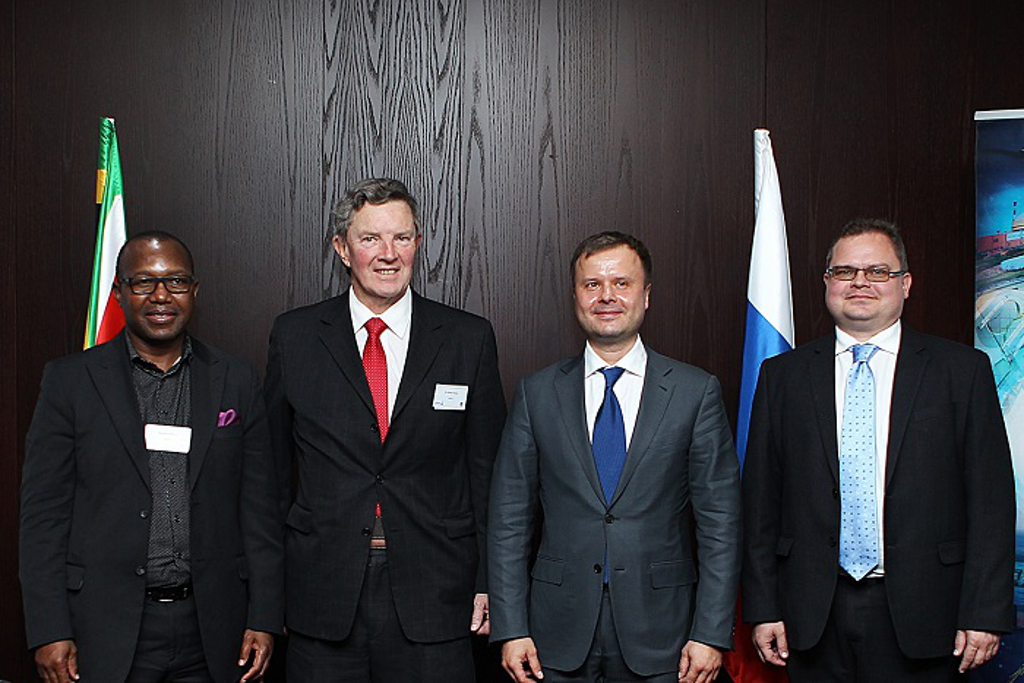
back to contentsThe main area of cooperation identified in the document is that of nuclear medicine and particularly cancer treatment in Africa and abroad. Rusatom Healthcare and NECSA intend to build two solution reactors in the Republic of South Africa. The reactors will be used for medical isotope production. The parties also plan to construct a commercial cyclotron in South Africa to further increase the production capacity of nuclear medicine in the region. A cyclotron is another cost effective method of producing various radiopharmaceuticals.
“Both parties have a great deal of expertise in this sector and we believe that a combined effort will open up new markets and hasten new technological advancements in the sector. Nuclear medicine is rapidly expanding globally and plays a vitally important role in the early detection of cancers and other non-communicable diseases,” director general of Rusatom Healthcare Denis Cherednichenko said.
“We have long been planning a massive expansion of our nuclear medicine operations and look forward to exploring these opportunities with our Russian counterparts,“ Chairman of NECSA Kelvin Kemm replied.
According to the CEO of NECSA Phumzile Tshelane, nuclear medicine is the most effective method of early cancer detection. And the earlier cancer is deiagnosed, the more likely it is to respond positively to treatment, which generally results in a greater probability of recovery.
“Nuclear medicine not only saves lives, but also generates a large revenue for South Africa. NECSA is looking forward to increased production and the maximization of profits for the country,” Phumzile Tshelane noted.
For reference:
NECSA is recognized as a world leader in the production or nuclear medicine and exports these lifesaving radiopharmaceuticals to over 60 countries on a daily basis, with an annual turnover of in excess of a billion Rand (around 75 mln USD).
Solution reactors consist of an enriched uranium salt dissolved in water and acid and contained in shielded tank or vessel. Approximately 30 solution reactors have been built world-wide and operated over many years since the beginning of modern nuclear programmes in the 1940s and 1950s. Most of these reactors are no longer in service. However, in the 1990s a renewed interest in solution reactors for the production of medical isotopes has prompted several countries, including China, the Russian Federation and the United States of America.