Quality Assured
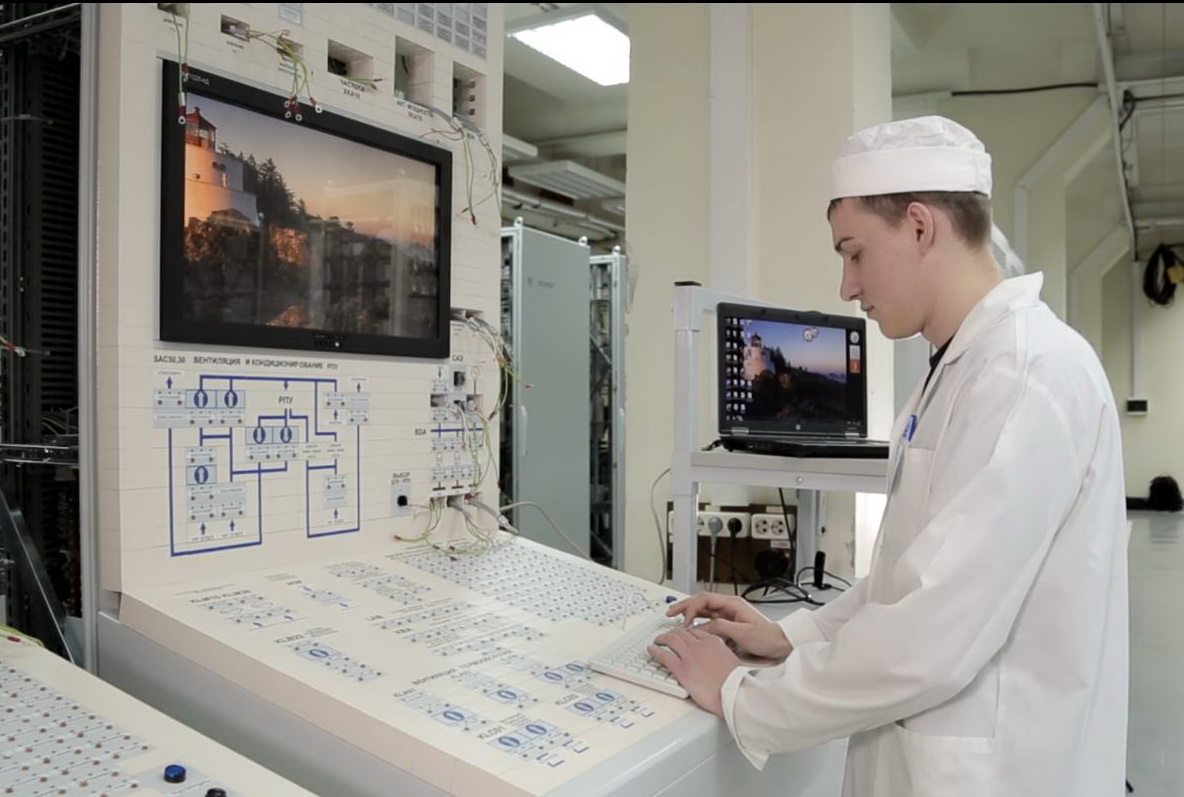
back to contentsUpper-level software and hardware components of the automated control systems for Kudankulam Units 3 and 4 passed quality testing at Rosatom’s subsidiary in Nizhny Novgorod (Russia) and were found compliant with technical specifications.
“Preliminary tests began in May 2018. We kept the entire process in check and followed technical requirements to meet project specifications. Commercial production will begin early next year on the basis of existing prototype. The tests will make it much easier to produce control systems for Kudankulam Units 5 and 6 because they will have the same design,” said Evgeny Zolotaryov, Manager of the Kudankulam Control System Project at RASU (a Rosatom Group integrator for automated control systems).
The Kudankulam NPP construction project is key to civil nuclear cooperation between Russia and India. The nuclear plant is being built in the state of Tamil Nadu (South India) and will consist of six nuclear power units with VVER-1000 reactors. The project was commissioned by the Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL). Construction started in 2002 under the supervision of Rosatom’s subsidiary ASE. Units 1 and 2 of Kudankulam NPP are already connected to the grid. In 2017, the first concrete was poured at Units 3 and 4, which are scheduled for commissioning in 2023 and 2024 respectively. Preparations are underway at Units 5 and 6, with the first concrete expected to be poured in 2019 and 2020.
On October 5, a document on further civil nuclear cooperation between Russia and India was signed on the margins of the 19th Russian-Indian Summit held in New Delhi. The parties declared their intention to build six Russian-designed power units at a new site in India, expand cooperation in third countries, and join efforts in other promising nuclear fields apart from power reactor construction. Russia will offer India a Generation 3+ VVER reactor design and plans to increase local content in machinery and equipment for the new power plant.