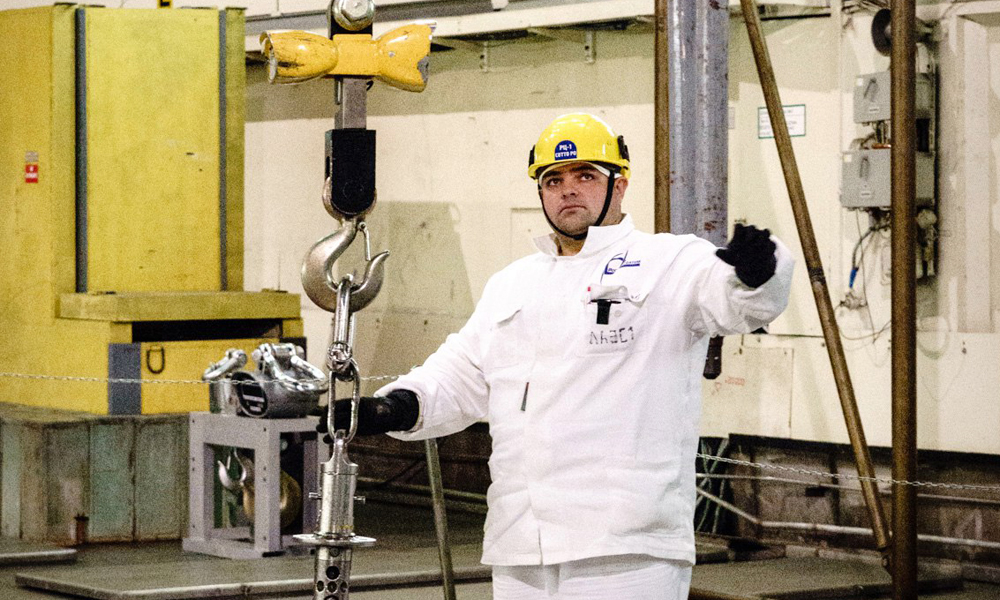
Leningrad Nuclear Plant Contributes to Fighting Cancer
back to contentsThe isotopes were shipped to the Karpov Institute of Physical Chemistry. The contract between the parties provides for a weekly delivery of 4 to 6 containers with a radioactivity of 70–80 Ci. This amount is enough to perform 2,000 to 3,000 cancer diagnostic and treatment procedures every week. “These isotopes have a half-life of 8 hours. It means that their radioactivity will decrease twofold in 8 hours after they are removed from the reactor. This is why our logistics is thoroughly planned so that not to waste a single minute,” says Evgeny Gorbunov, Head of Radiation Technology Department at the Leningrad Nuclear Power Plant. “We cannot afford delays as they may impair the quality of radiopharmaceuticals.”
“The global demand for radiopharmaceuticals is steadily growing as possibilities of the nuclear medicine are being explored and put to use. Despite competition, the Leningrad Nuclear Power Plant has three advantages. We have 4 reactors, which can perform irradiation by turns to ensure non-stop production and seamless supplies. Our reactor cores are spacious enough to irradiate a large number of containers at a time. Lastly, we have low production costs,” NPP Director Vladimir Pereguda says.
The plant owes its isotope fabrication capacity to the unique design of RBMK reactors having irradiation channels. When producing iodine-131, the channels are loaded with capsules containing natural tellurium dioxide. It takes two weeks to obtain iodine-131, which can be used in radiopharmaceuticals. The plant specializes in irradiation of starting materials. This technology is economically more beneficial as it is standardized and does not require extensive staff.
The global market is short of capacity to irradiate targets for the production of isotopes. Alongside iodine-131, the Leningrad Nuclear Power Plant fabricates cobalt-60, iodine-125, molybdenum-99, and dopes silicon. Since 1992, the plant has been supplying the Khlopin Radium Institute with medical radionuclides used to perform nearly 3,000 diagnostic procedures a year. “At present, St. Petersburg has 7 or 8 clinics that operate tomography scanners for cancer diagnostics. All of them use our isotopes. We sell molybdenum for the money that the St. Petersburg Healthcare Committee can afford to pay, not what it actually costs. This money is not a big deal for us. Isotopes are more of a charity than a business,” Evgeny Gorbunov noted.
Integrating nuclear medicine solutions
Rosatom is heavily engaged in the development of nuclear medicine, which is now the company’s rapidly growing standalone business. Rosatom Group companies manufacture a range of medical equipment and isotopes. Not long ago, Rosatom set up the production of molybdenum-99, an isotope that is widely used in cancer treatment. Almost 80% of all procedures in nuclear medicine are dependent on supplies of molybdenum-99, an important radionuclide used for extraction of technetium-99m (Тс-99m), a key diagnostic radiotracer in the present-day nuclear medicine. Tc-99m is helpful in diagnosing a wide range of human conditions, first and foremost cancer and cardiovascular diseases. The total number of Tc-99m involving diagnostic procedures in the world exceeds 25 million per year. Russian-made medical isotopes are now supplied to other countries.
Rosatom has also established a new division – Rusatom Healthcare – to foster the development of nuclear medicine. It is set to act as an integrator of commercial products and services in nuclear medicine and irradiation technology. Its purpose is to market comprehensive nuclear medicine and commercial irradiation solutions. Rosatom often spins off a particular line of business to create a dedicated responsibility center. Rusatom Healthcare is an integrated responsibility center in charge of nuclear medicine and commercial irradiation technologies.
The division includes Isotope, Rosatom’s Research Institute of Applied Physics and Automation, Karpov Institute of Physical Chemistry, United Innovation Corporation, RusReaktor, Center for Advanced Diagnostics, Snezhinsk Nuclear Medical Technologies and others. It works closely with many of Rosatom Group companies, particularly those involved in the production or innovative treatment and processing of various components for nuclear medicine. All these companies have vast experience and competencies, hundreds of highly qualified professionals, unique technologies and patents. Today, Rusatom Healthcare offers an integrated turn-key solution for nuclear medicine centers. The offering includes design, construction and maintenance of such facilities throughout their entire life cycle.