Turkish Start
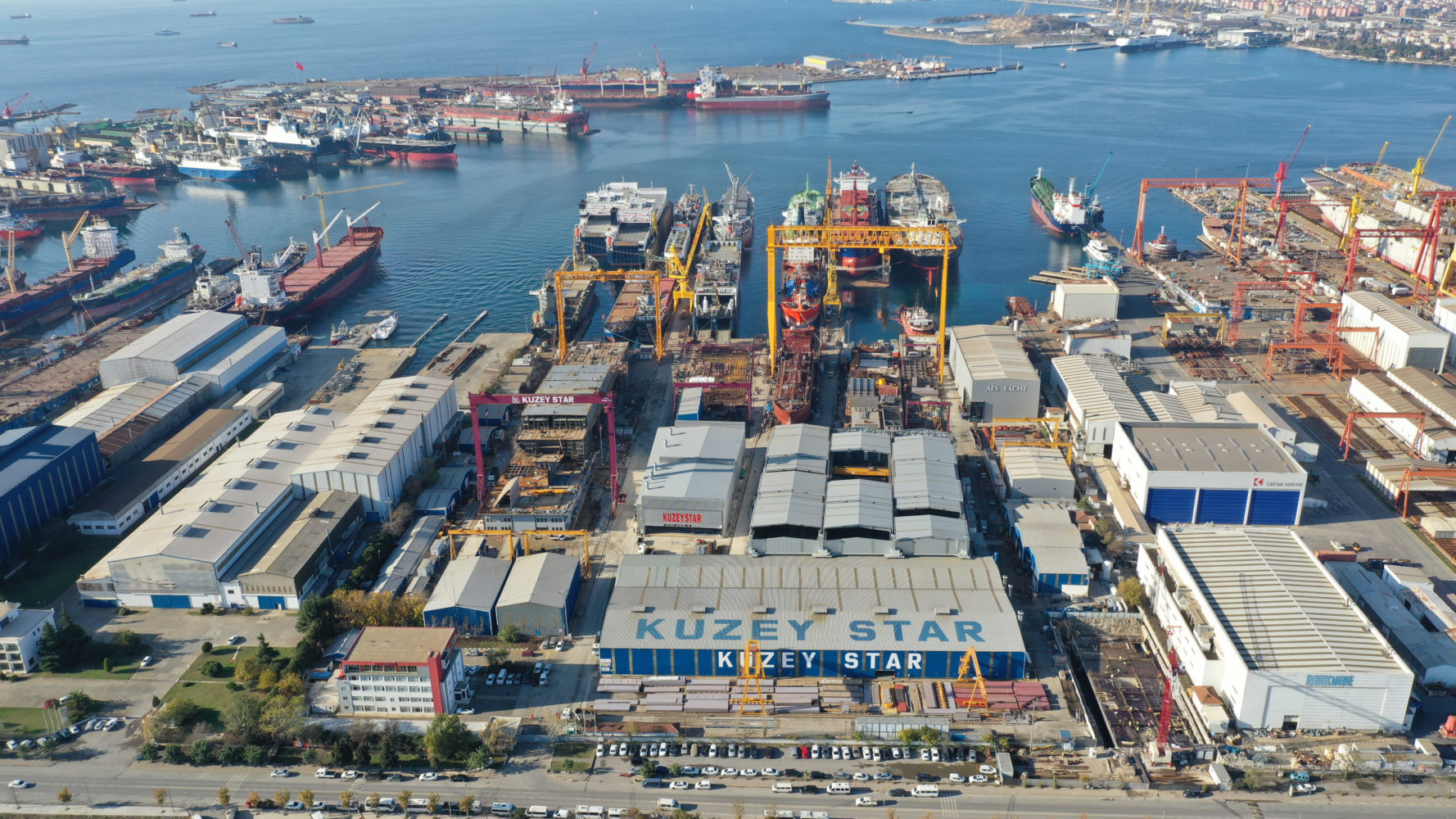
back to contentsOn March 15, the Istanbul-based Kuzey Star Shipyard hosted a keel laying ceremony for a floating dock that will service Russian-designed Project 22220 multi-purpose nuclear icebreakers.
Atomflot and Kuzey Star signed a construction contract for the floating dock in June 2021. “The Turkish shipyard has all the necessary competencies and earned a respectable reputation in the shipbuilding market,” said Mustafa Kashka, the then CEO of Atomflot. The deal is worth almost RUB 5 billion. According to the contract, the dock will be built and delivered to Murmansk within 29 months after the date of signing. The sea voyage from Istanbul to Atomflot’s naval base is estimated to take at least one month.
Atomflot has two floating docks for now. One of them, PD-3, is stationed in the port of Murmansk. It is used to dock the nuclear icebreaker 50 Let Pobedy and third-party vessels. The other dock, PD-0002, is stationed at Atomflot’s base and services Yamal, Taymyr and Vaygach nuclear icebreakers.
However, those floating docks are not capable of servicing Project 22220 series icebreakers (Arktika and Sibir are already in operation; the other three – Ural, Yakutia and Chukotka – will join them soon). For instance, the breadth of PD-0002 is 33.5 meters while the breadth of the new icebreakers is 34 meters. Without a floating dock, the new icebreakers are repaired in the dry dock of the Kronstadt Marine Plant (this is where Arktika was serviced in 2021). All the operations, including transportation, require administrative efforts, entail costs and consume time. This is why the decision was made to build a new floating dock.
The new floating dock will have a capacity of around 30,000 tons. To compare, PD-0002 has a capacity of about 20,800 tons while the lightship mass of Project 22220 icebreakers is 26,700 tons. The steel floating dock will have two towers and a pontoon system that operates as a single pontoon. The towers are steel boxlike structures attached to the dock pontoons on two sides. They contain key mechanisms and functional systems of the floating dock. When docking, a section of the towers submerges while the rest stays above water, ensuring positive buoyancy.
The new dock is designed to repair underbodies, sea valves, steering and anchoring gear of Atomflot’s new icebreakers, clean and paint the hulls, replace hull protection, and carry out other repair and maintenance works. The key advantage of the floating dock over dry docks is its mobility. It can be installed anywhere offshore where the water depth is sufficient. Building a dry dock requires much more time and effort since it needs a large parcel of land to sit on and a large amount of construction works.
The new dock is expected to replace PD-3. It will service not only Project 22220 icebreakers but also other nuclear icebreakers, which are now in operation (50 Let Pobedy, Yamal, Taymyr, and Vaygach).
The construction of the new floating dock is going as scheduled. “Compliance with construction deadlines is extremely important for us. The floating dock is an essential element of the coastal infrastructure for the maintenance of Project 22220 nuclear icebreakers,” Mustafa Kashka pointed out.
In the future, Atomflot will need one more floating dock, this time for Rossiya, the first Project 10510 icebreaker. Its capacity should be no less than 60,000 tons.
The overarching purpose of Project 22220 and Project 10510 icebreakers is to ensure uninterrupted year-round navigation on the Northern Sea Route (NSR), which is expected to be launched in 2030.
The NSR Directorate is preparing actively for the extension of navigation and traffic growth. Apart from construction of nuclear icebreakers, this covers improvements of the navigation, including digital, infrastructure. In particular, a single digital platform will be created to integrate both new and existing solutions developed by the NSR Directorate, cargo and ship owners, Russian Meteorological Service, and Ministry for Development of Russian Far East. The platform will go online in 2025.
Last year, buoys equipped with automatic identification stations were installed along the NSR. Their operation will be analyzed and improved. The NSR Directorate conducts offshore and bathymetric surveys and studies ice conditions (ice thickness and movement) in the eastern section of the Northern Sea Route, which has never been crossed in winter before. The Directorate also builds onshore facilities for the Utrenniy terminal and in Sabetta, a sea port in the Gulf of Ob.

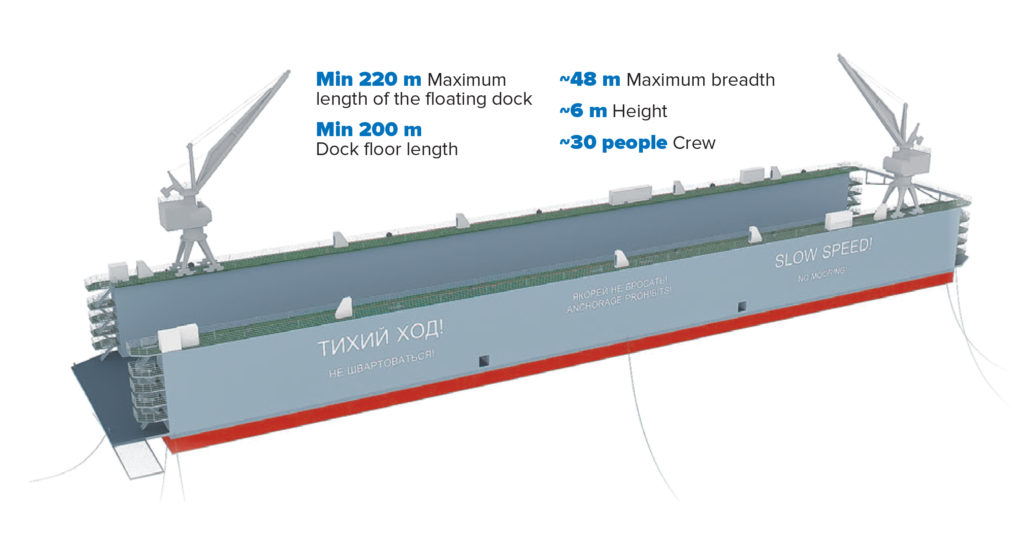
FACTS & FIGURES
Min 220 m Maximum length of the floating dock
Min 200 m Dock floor length
~ 48 m Maximum breadth
~ 6 m Height
~ 30 people Crew