Prioritizing Resilience
back to contentsAll construction and installation works are fully on track at the site of Turkey’s first nuclear power plant. The plant is growing in leaps and bounds. Experts are confident the facility will adhere to the highest safety standards.
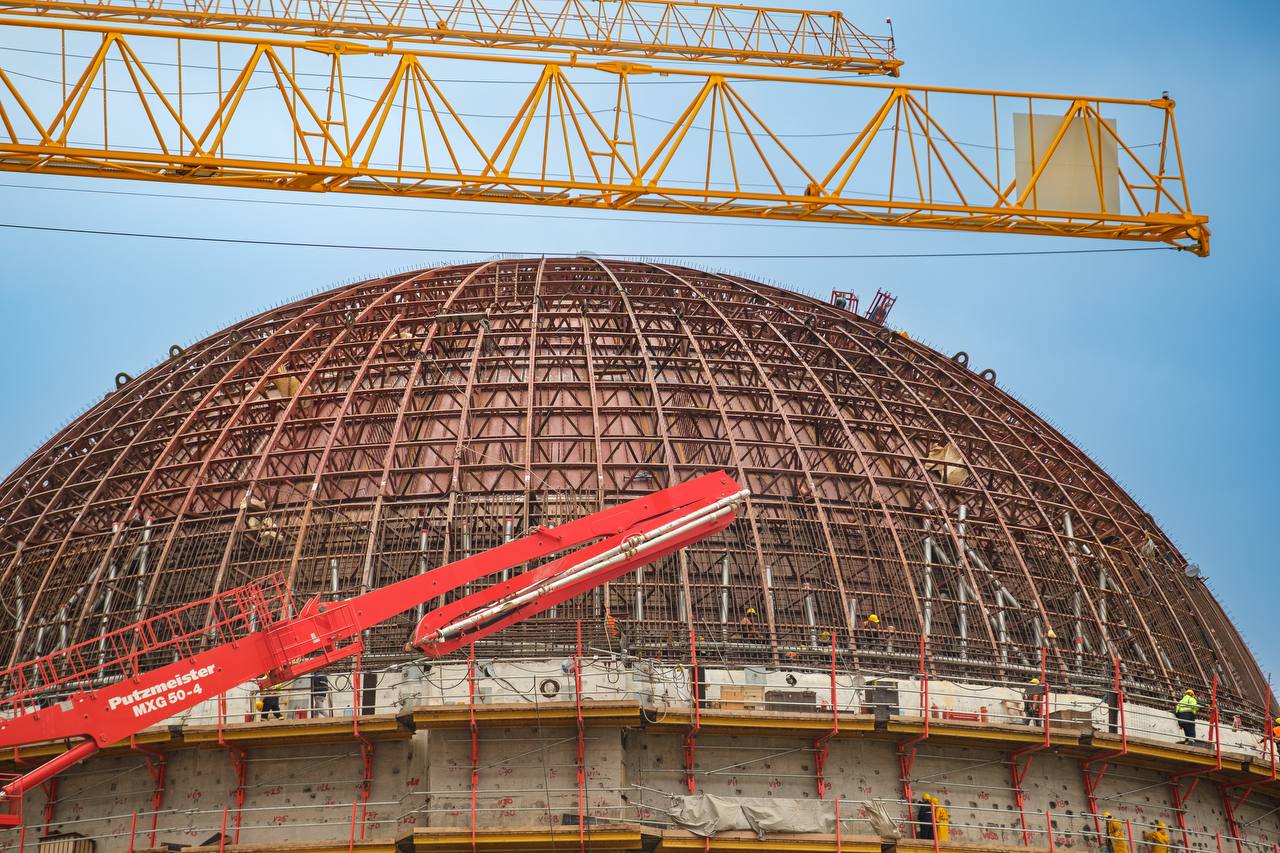
In April, the fourth tier of the internal containment shell, which is one of the key components of the nuclear plant’s safety systems, was installed in the reactor building of Akkuyu Unit 2. Made of a special concrete mix and lined with steel sheets, the containment isolates the reactor compartment and serves as a support for pipeline penetrations and a polar crane.
“The fourth tier is the last cylindrical one, followed by a dome, which is planned to be installed this summer. After that we will proceed with welding of the third and fourth tiers, reinforcement, and installation of embedded parts, including parts of the airlocks for vehicles and personnel,” Sergey Butskikh, First Deputy CEO at Akkuyu Nuclear and Director of the under-construction Akkuyu NPP, commented.
Meanwhile, installation of the roof was completed at Unit 1 in three months. The roof of the turbine hall consists of nine large trusses with a total weight of over 1,100 tons. The trusses were pre-assembled right on the construction site, simultaneously on two assembly stands, and put in place using a Liebherr crawler crane.
“Mounting the roof trusses of the turbine building is a complex and time-consuming operation that requires careful preparation. Each truss is installed with an accuracy of up to ten millimeters. The team of builders and installers got things done properly despite the tight schedule and challenging weather conditions,” Sergey Butskikh said.
Construction and installation works are going on at every corner of the construction site, encompassing main and auxiliary facilities of the nuclear power plant – four power units, onshore hydraulic structures, power evacuation systems, administrative buildings, a training center, and security facilities.
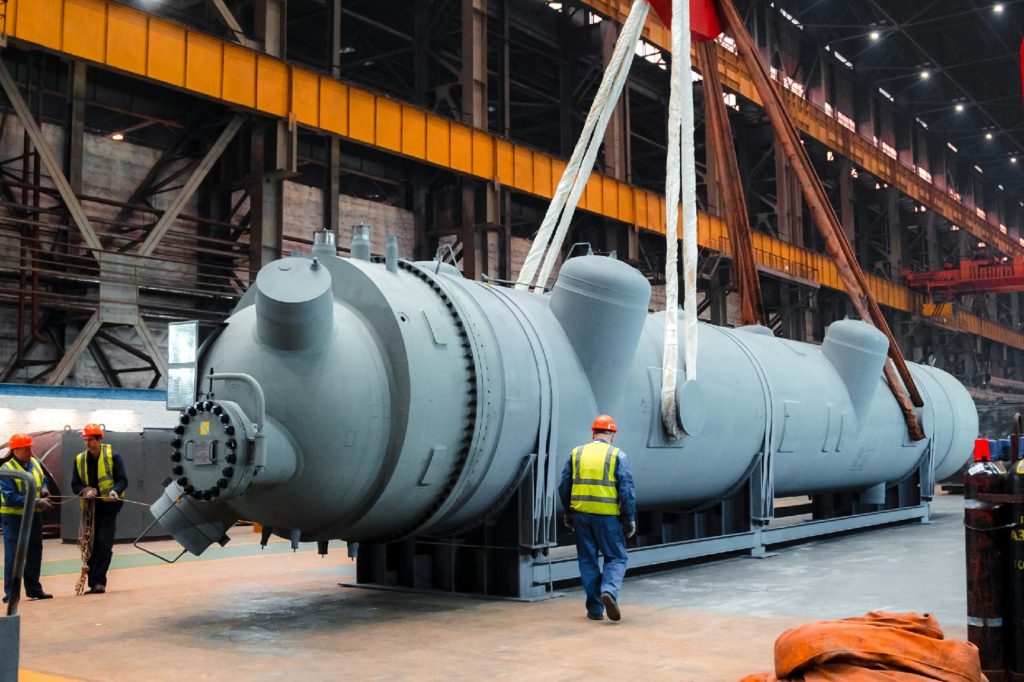
Russian companies are manufacturing all the necessary equipment for the future plant. In April, ZiO-Podolsk (part of Rosatom’s power engineering division AtomEnergoMash) manufactured and shipped the second low-pressure heater for Akkuyu Unit 1. The first heater was shipped in March. These are the most sophisticated pieces in the entire scope of equipment produced at ZiO-Podolsk. The heaters are horizontal surface heat exchangers connected in parallel to each other. They are installed in the transmission duct of the turbine main condenser to preheat primary condensate and keep it heated at the required temperature.
In March, fuel components for the Akkuyu NPP passed acceptance inspection at Elemash (part of Rosatom’s fuel division). Accepted were absorbers and fuel elements containing uranium dioxide and gadolinium oxide and intended for the production of fuel assemblies. “Representatives of the Turkish nuclear regulator praised the well-coordinated and professional work in every department of Elemash,” said Ivan Pchelin, Deputy CEO at Elemash.

Russia helps Turkey train personnel for the nuclear industry. On April 1, the National Nuclear Research University (MEPhI, Rosatom’s backbone university) completed the admission of students for a three-year master’s program in nuclear physics and technology. During the first year, the students will study technical Russian; the next two years will be dedicated to the specialty subjects.
“Training highly qualified Turkish personnel for the nuclear industry is one of the priorities of the Akkuyu project. Over 300 young engineers are already working at the construction site of Turkey’s first nuclear power plant and gaining invaluable experience that will help them when the Akkuyu NPP is in operation,” Akkuyu Nuclear CEO Anastasia Zoteeva commented.
Also in April, Akkuyu Nuclear organized a traditional creative competition for the children aged 6 to 16 to celebrate the National Sovereignty and Children’s Day. Children from all over Turkey took part in that nationwide competition. This year, the contest featured new categories, including an Energetic Century video and an Atomic Superhero drawing. The winners received valuable gifts.
Turkey is recovering from the earthquakes that affected 11 provinces. The country is continuing to publicly discuss potential impacts of natural disasters on the operation of the under-construction nuclear power plant. Experts are confident the Akkuyu NPP is located in the safest possible place.
According to Prof. Dr. Shakir Shahin, a lecturer at the Chair of Seismology, Department of Geophysical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering at Suleyman Demirel University, the Akkuyu site is located in a low seismic risk area. “This area is located in the zone of Devonian rocks. In other words, it has solid ground,” Shahin noted. The professor stressed there were no active fault lines within 100 kilometers of the Akkuyu NPP construction site and the power plant was being built 10.5 meters above the sea level, which served as an additional precaution against tsunami.
Prof. Dr. Şule Ergün from the Nuclear Energy Engineering Department at Hacettepe University recalled that safety had always been a top priority in the Russian-designed nuclear power plants with Generation 3+ VVER-1200 reactors. “In addition to active safety systems, these nuclear power plants are equipped with passive systems that need no power supply, operator intervention, or automatic protection systems against the negative consequences of a strong earthquake and tsunami. Structural tests and inspections conducted at the Akkuyu NPP demonstrate compliance with the safety requirements and an ability to withstand extreme external impacts,” Prof. Ergün stressed.
TVEL is Rosatom’s fuel division and one of the world’s largest suppliers of nuclear fuel. TVEL is a monopoly supplier of nuclear fuel to all power, marine and research reactors in Russia. The company fuels nuclear power plants in 15 countries, or every sixth power reactor in the world.
AtomEnergoMash (AEM) is Rosatom’s power engineering division and one of Russia’s largest power machinery producers providing comprehensive solutions in design, manufacture and supply of machinery and equipment for nuclear, thermal, petroleum, shipbuilding and steel-making industries.